How to operate a drone? It’s a question sparking curiosity in countless individuals, from hobbyists captivated by aerial photography to professionals leveraging drones for diverse applications. This guide delves into the intricacies of safe and effective drone operation, covering pre-flight checks, control mastery, flight modes, aerial photography techniques, troubleshooting, and legal compliance. Understanding these elements is crucial for responsible and enjoyable drone usage.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or seeking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the exciting world of drone piloting. We’ll cover everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, ensuring you’re well-prepared for your aerial adventures.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and responsible drone operation. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and legal issues. This section details the necessary steps and safety considerations.
Pre-Flight Inspection
Before each flight, a comprehensive inspection is mandatory. This involves several key steps to ensure your drone is in optimal condition.
- Battery Check: Verify battery charge level using the drone’s battery indicator or a separate battery checker. Ensure the battery is properly connected and free from any visible damage.
- Propeller Inspection: Carefully examine each propeller for cracks, bends, or other damage. Replace any damaged propellers before flight.
- GPS Signal Acquisition: Allow sufficient time for the drone to acquire a strong GPS signal before takeoff. This ensures accurate positioning and stability during flight.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire drone, checking for any loose parts, damage, or obstructions.
- Gimbal Check (if applicable): Verify that the gimbal is functioning correctly and is properly secured.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount for responsible drone operation. Failure to do so can result in fines, accidents, and legal repercussions.
- Always maintain visual line of sight (VLOS): Never fly your drone beyond your visual range.
- Avoid flying near airports, helipads, or other restricted airspace: Check local airspace regulations before each flight.
- Respect privacy: Do not fly your drone over private property without permission.
- Fly responsibly: Avoid flying your drone in crowded areas or near people.
- Be aware of weather conditions: Do not fly your drone in adverse weather conditions such as strong winds, rain, or snow.
Drone Battery Comparison, How to operate a drone
| Battery Type | Voltage | Flight Time (Approximate) | Safety Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium Polymer (LiPo) | 7.4V – 14.8V (common) | 15-30 minutes (varies by drone and usage) | Overcharge protection, low voltage alarm, thermal cutoff |
| Lithium Ion (Li-ion) | 7.4V – 14.8V (common) | 15-30 minutes (varies by drone and usage) | Overcharge protection, low voltage alarm, thermal cutoff |
| Intelligent Flight Battery (IFB) | Varies by manufacturer | Varies by manufacturer | Integrated battery management system (BMS) with multiple safety features |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section will guide you through the various control methods and maneuvering techniques.
Drone Control Methods
Most drones utilize either a dedicated remote controller or a mobile app for control. Each method offers unique advantages and disadvantages.
- Dedicated Remote Controller: Offers precise control and tactile feedback, ideal for experienced pilots.
- Mobile App Control: Provides a user-friendly interface, suitable for beginners but may lack the precision of a dedicated controller.
Standard Drone Controller Functions
A typical drone controller features two joysticks, several buttons, and switches. Each element controls specific aspects of the drone’s flight.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the basics, which you can do by checking out this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From there, practice in a safe, open area is key to mastering the skills needed for confident and responsible drone operation.
- Left Joystick: Controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude).
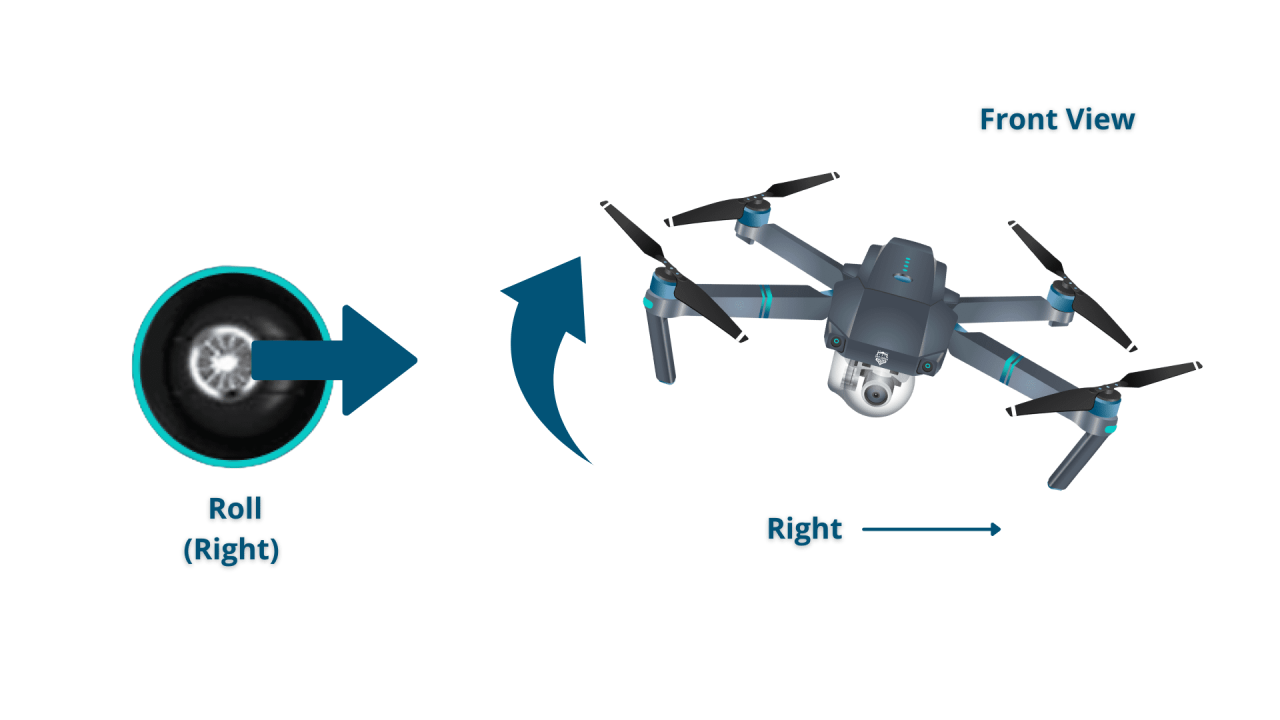
- Right Joystick: Controls pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement).
- Buttons and Switches: Control various functions such as camera settings, return-to-home (RTH), and flight mode selection.
Mastering Drone Maneuvering
Proficient drone piloting involves mastering several key maneuvers. Practice is crucial for developing the necessary skills and coordination.
- Takeoff and Landing: Execute smooth and controlled takeoffs and landings in a safe, open area.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable hover position without drifting or swaying.
- Directional Control: Accurately control the drone’s movement in all directions.
Drone Compass and GPS Calibration
Regular calibration ensures accurate navigation and stability. This process helps the drone orient itself correctly.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to safely and effectively navigate your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, proficient drone operation requires practice and a thorough understanding of safety regulations.
- Compass Calibration: Follow the instructions in your drone’s manual to calibrate the compass. This usually involves rotating the drone in a figure-eight pattern.
- GPS Calibration: Allow the drone sufficient time to acquire a strong GPS signal before each flight. This ensures accurate positioning and helps prevent drift.
Flight Modes and Features
Understanding different flight modes is essential for adapting to various situations and maximizing your drone’s capabilities. Each mode offers specific advantages and disadvantages.
Flight Mode Comparison
| Flight Mode | Description | Features | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limits speed and responsiveness for easier control. | Reduced speed, stability assistance | Beginners, learning to fly |
| Sport Mode | Unlocks full speed and responsiveness for more dynamic flight. | Increased speed, agility | Experienced pilots, aerial acrobatics |
| GPS Mode | Utilizes GPS for precise positioning and stability. | GPS-assisted flight, return-to-home (RTH) | Long-range flights, precise aerial photography |
| Attitude Mode | Maintains drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, regardless of GPS signal. | Orientation control without GPS reliance | Indoor flying, GPS-challenged environments |
Advanced Drone Features
Many drones offer advanced features that enhance flight capabilities and creative possibilities.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point.
- Waypoint Navigation: Allows you to program a flight path with pre-defined points.
- Follow-Me Mode: The drone automatically follows a designated subject.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing stunning aerial imagery requires understanding key photographic principles and adjusting camera settings appropriately. This section provides guidance on achieving high-quality results.
Principles of Aerial Photography and Videography
Achieving high-quality aerial photos and videos involves understanding and applying several key principles, including composition, lighting, and camera settings.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques to create visually appealing images.
- Lighting: Consider the time of day and weather conditions to achieve optimal lighting. The “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) often provides the most aesthetically pleasing light.
- Camera Settings: Adjust ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to achieve the desired depth of field, exposure, and motion blur.
Capturing Different Shot Types
Experimenting with various camera angles and movements can significantly enhance the visual appeal of your aerial content. Consider these techniques:
- Panoramas: Capture a wide, sweeping view by stitching together multiple overlapping images.
- Cinematic Movements: Use smooth, deliberate movements to create a sense of fluidity and dynamism. Avoid jerky or abrupt changes in position.
- Aerial Perspectives: Experiment with different altitudes and angles to capture unique perspectives.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for maintaining optimal drone performance and longevity. This section provides guidance on addressing common issues.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Several common issues can arise during drone operation. Understanding the causes and solutions can prevent significant problems.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully before each flight. Avoid completely depleting the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure a clear view of the sky for optimal GPS signal reception. Avoid flying in areas with significant obstructions.
- Motor Issues: Inspect motors for damage or debris. Replace any faulty motors.
Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance helps prevent issues and extends the lifespan of your drone.
- Clean the drone: Remove any dirt, debris, or dust from the drone’s body and propellers.
- Inspect propellers: Check for cracks, damage, or imbalance.
- Check battery health: Regularly monitor battery charge cycles and health.
Troubleshooting a Drone That Won’t Take Off
A flowchart could visually represent this process, but a textual representation is provided here.
- Check battery level. Is it fully charged? If yes, proceed to step 2; if no, charge the battery.
- Check propeller condition. Are propellers damaged or improperly installed? If yes, repair or replace; if no, proceed to step 3.
- Check GPS signal. Is the GPS signal strong? If yes, proceed to step 4; if no, move to an open area with a clear view of the sky.
- Check for any error messages on the controller or app. Consult the manual for troubleshooting the specific error.
- Check motor functionality. Are the motors spinning freely? If no, consult the manual or seek professional assistance.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and adhering to local drone regulations is crucial for legal and safe operation. This section provides guidance on navigating these requirements.
Importance of Adhering to Regulations
Flying a drone without adhering to regulations can lead to fines, legal action, and even criminal charges. It is essential to understand and comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
Resources for Checking Airspace Restrictions
Numerous resources are available to help you determine airspace restrictions and obtain necessary permits.
- FAA DroneZone (USA): Provides information on airspace restrictions and registration requirements.
- Local aviation authorities: Contact your local aviation authority for specific information on airspace restrictions in your area.
Legal Implications of Non-Compliance
Violating drone regulations can have serious consequences, including hefty fines, suspension of flying privileges, and potential criminal charges.
Summary of Key Legal Requirements

| Location | Requirement | Penalty for Violation | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | FAA registration, airspace awareness | Fines, imprisonment | Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) |
| UK | CAA registration, drone license (for commercial use) | Fines, imprisonment | Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) |
| Canada | Transport Canada registration, airspace awareness | Fines, imprisonment | Transport Canada |
Mastering drone operation involves a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of pre-flight procedures, control mechanisms, flight modes, and legal considerations. Remember, consistent practice and adherence to safety regulations are paramount. By integrating these principles, you can unlock the full potential of your drone while ensuring responsible and enjoyable aerial experiences.
Safe flying!
Helpful Answers
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS and beginner modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
Charge your drone battery after each flight and avoid fully depleting it. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for optimal charging practices.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to manual control and attempt to return it to a safe location. Avoid flying in areas with poor GPS reception.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures.
